Heart Rate 101: Everything You Need to Know About Monitoring Your Heart
Complete beginner's guide to understanding and tracking your heart rate effectively.

Introduction
Your heart rate is a key indicator of your overall health. Whether you're just starting to explore fitness or simply want to better understand your body, monitoring your heart rate can provide essential insights. In this beginner-friendly guide, we'll cover everything you need to know about heart rate, from its basics to practical tracking tips.
What Is Heart Rate?
Heart rate refers to the number of times your heart beats per minute (BPM). It fluctuates throughout the day based on your activity level, emotional state, and overall health.
Key Terms to Know

Resting Heart Rate (RHR):
Your heart rate when you're calm and at rest
Maximum Heart Rate (MHR):
The highest number of beats your heart can reach during maximum effort
Target Heart Rate:
The optimal range your heart should be in during exercise to achieve your fitness goals
Why Is Heart Rate Important?

Monitoring your heart rate provides valuable insights into your cardiovascular health and fitness.
Track Fitness Progress
Lower resting heart rate over time indicates improved cardiovascular fitness
Optimize Workouts
Staying in your target heart rate zone helps you burn calories efficiently
Detect Issues
Sudden changes in heart rate can signal potential health concerns
How to Measure Your Heart Rate

Manual Method
1. Find Your Pulse
Place your index and middle fingers on your wrist (radial artery) or neck (carotid artery)
2. Count the Beats
Count the number of beats in 30 seconds and multiply by 2 to get your BPM
Using Technology
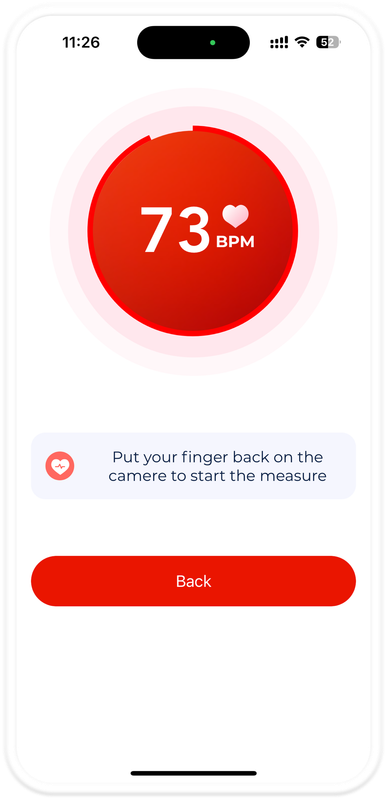
Mobile Apps
Apps like Impulse Heart Health Monitor use your phone's camera
Chest Straps
For precise tracking during exercise
Wearables
Smartwatches and fitness trackers monitor heart rate continuously
Normal Heart Rate Ranges
Resting Heart Rate by Age
| Age Group | Normal RHR (BPM) | Athletic RHR (BPM). |
|---|---|---|
| Children (6-15 years) | 70-100 | 60-80 |
| Adults (18-64 years) | 60-100 | 40-60 |
| Seniors (65+ years) | 70-100 | 50-70 |
Heart Rate Zones Overview
Zone 1: Very Light (50-60% MHR)
Perfect for warm-ups and recovery. Helps improve overall health and build basic endurance.
Zone 2: Light (60-70% MHR)
The "fat burning" zone. Great for building aerobic fitness and endurance.
Zone 3: Moderate (70-80% MHR)
Improves aerobic fitness and speed. You're working but can still hold a conversation.
Zone 4: Hard (80-90% MHR)
Increases maximum performance capacity. You're breathing heavily.
Zone 5: Maximum (90-100% MHR)
For very short intervals. Helps top athletes improve speed and power.
Practical Monitoring Tips
Best Practices for Heart Rate Monitoring
1. Consistency is Key
Measure at the same time each day, preferably in the morning before getting out of bed
2. Use the Right Tools
Choose accurate devices and apps for monitoring
3. Track and Analyze
Keep a log of your measurements to spot trends and changes
Signs of Abnormal Heart Rate
Warning Signs to Watch For
- Consistently high resting heart rate (above 100 BPM)
- Irregular heartbeats or palpitations
- Dizziness or shortness of breath
Frequently Asked Questions

Q: How often should I check my heart rate?
A: For general health monitoring, check your resting heart rate daily, preferably in the morning. During exercise, continuous monitoring can help you stay in your target zone.
Q: What affects heart rate besides exercise?
A: Many factors can influence your heart rate, including stress, temperature, body position, medications, and even the time of day.
Q: How can I lower my resting heart rate?
A: Regular cardiovascular exercise, stress management, good sleep habits, and maintaining a healthy weight can help lower your resting heart rate over time.
Getting Started

Download Impulse App Today. Take control of your heart health with our free, easy-to-use app.
Disclaimer
The information provided in this article is for informational purposes only and is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult your doctor or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding your health or a medical condition. Never disregard or delay seeking professional medical advice because of something you have read in this article.